How Bad Is the Physician Shortage?
Rural and Low-Income Areas
Now Face Crisis Levels
Did you know…
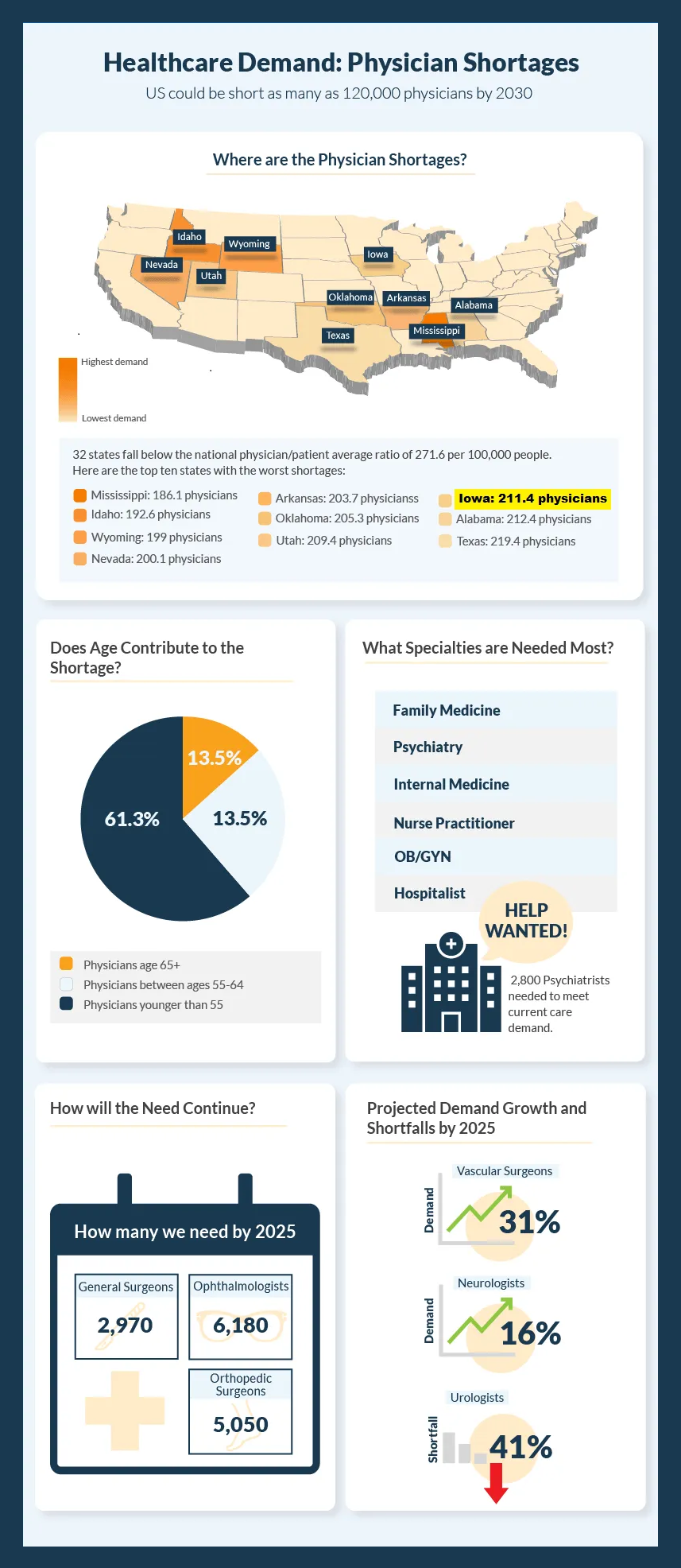
- In 2021, there was a shortage of about 46,000 doctors in the U.S.
- By 2034, that number is expected to climb as high as 124,000; up to 48,000 of these will be primary care physicians.
- Rural and low-income areas will be hardest hit by the increasing doctor shortage.
- About 40% of Iowans reside within the 77 counties currently designated as “rural,” and are medically underserved.
In June of 2021, the AAMC (Association of American Medical Colleges) released its latest report on the impending U.S. physician shortage, and the picture looks pretty bleak. Even before COVID hit, our country was facing a potentially serious doctor shortage; the pandemic has only exacerbated the workforce challenge. Here are the reasons most often cited for this shortfall:
Growing U.S. Population
The U.S. population increased by nearly 8% over the past decade. That's the slowest growth rate since the 1930s, and yet it still represents an increase of almost 27 million people. And while the U.S. birth rate dipped by 4% during the pandemic, an increase in immigration resulted in overall population growth.
The U.S. population increased by nearly 8% over the past decade. That's the slowest growth rate since the 1930s, and yet it still represents an increase of almost 27 million people. And while the U.S. birth rate dipped by 4% during the pandemic, an increase in immigration resulted in overall population growth.

What Is an HPSA?
The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) federally designates geographic areas, populations, or facilities that suffer from an acute shortage of health care providers as HPSAs (Health Professional Shortage Areas).
In doing so, HHS uses three criteria to identify these groups:
- Ratio of population to provider
- Percentage of population with income below the Federal Poverty Level
- Travel time to the nearest healthcare source outside the HPSA.
In 2020, Iowa had a total of
353 HPSAs
for primary care, mental health, and dental care. Nationally, more than 20,000 HPSAs have been designated.
In October of 2021,
HHS reported
that about 32,000 additional practitioners are needed to meet the needs of these communities.
Aging Population
More than 54 million Americans are currently age 65 and older. With 10,000 people joining their ranks every day, that number is projected to increase by about 18 million within the next decade. By 2032, seniors will outnumber children for the first time in U.S. history.
This aging population necessitates an increased demand for physician care. Older adults often suffer from multiple chronic health problems, such as heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, and hypertension. According to report by the National Institutes of Health, about 85% of senior adults suffer from at least one chronic condition that requires specific treatment and medical care.
Aging Physicians
It’s not just the population in general that’s aging. Ten percent of U.S. doctors are older than 65. The AAMC expects that number to double over the next decade. Right now, more than 30% of practicing physicians are over 60. Even so, physicians often delay retirement, compared to average American workers.
There are two reasons for this: 1) They’re in school for such a long time, they get a late start on developing their own practice, and 2) they usually enjoy their work.
However, as the number of older doctors starts to dwindle, the remaining practitioners can easily become stressed and overworked, as they endeavor to satisfy the demand for services. Burned-out physicians may choose to reduce their workloads in the interest of self-preservation.
Impact of COVID
And then there’s the crushing effect of COVID-19 on the U.S. healthcare community. In 2020, more than 3,600 medical staff members died from COVID, 17% of which – at least 613 – were doctors.
In addition to the fatalities, the ongoing battle with this pandemic continues to take a physical and emotional toll on physicians, leaving them fatigued and vulnerable to infection. More than a year later, Iowa hospitals are still routinely combatting the virus.
The economic uncertainties related to the pandemic also have taken a toll on physicians. During the height of the outbreak, thousands of practitioners called it quits. Both hospitals and doctors’ offices lost billions in revenue when elective medical procedures were suspended. At that time, surveys indicated that almost half of U.S. physicians were seriously reconsidering their career or practice.
--Article Continues Below--
Federal Cap on Residencies
The Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS) compensate hospitals every year to hire medical residents. The number of practitioners for any given year is ultimately determined by the number of residencies. The 1997 Balanced Budget Act established a cap on the number of annual residencies supported by CMS. Which means this funding has been frozen at 1996 levels for 25 years.
To address the issue, the Resident Physician Shortage Reduction Act of 2021
(HR 2256) was introduced in Congress last March. If approved, this bill would increase the number of residency positions paid by CMS by 2,000. Qualifying hospitals would include those in rural areas and HPSAs. HR 2256 is still under committee review.
Is There a Fix?
Experts have suggested several steps public health officials can take to equalize the distribution of healthcare services and help alleviate the physician shortage. These include:
- Promoting new technologies, including telemedicine.
- Recruiting more nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, and physician assistants, and expanding their scope of practice.
- Inducing providers to practice in shortage-prone areas by adjusting physician reimbursement policies.
- Encouraging retired physicians to reenter the workforce.
- Enabling medical students to graduate early.
- Encouraging medical school graduates to pursue residencies in primary care (e.g., internal medicine, pediatrics, and family medicine ) in the most medically disadvantaged areas.
- Advocating the passage of HR 2256 to increase the annual number of residencies paid by CMS.
Recent Posts










Share On: